Solar power continues to dominate new electricity capacity additions globally, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). As governments push climate targets and companies pursue decarbonisation strategies, investors are reassessing Top 5 Solar Stocks opportunities in 2026.

Solar stocks, spanning manufacturers, utilities, and technology providers, are central to this shift. This article reviews five widely tracked solar-linked equities across U.S. and Indian markets. It provides context on financial positioning, sector trends, and risks. It does not constitute investment advice.
Top 5 Solar Stocks in 2026: Market Context and Investment Drivers
Global solar installations have grown steadily over the past decade. According to the IEA’s renewable energy market analysis, solar accounted for the largest share of new power capacity additions in recent years. Falling module prices and supportive policy frameworks have strengthened deployment.
However, stock performance does not always mirror installation growth. Solar equities remain sensitive to interest rates, raw material costs, and regulatory changes.
“Solar companies operate within broader capital market cycles,” said an energy finance academic at the University of Oxford. “Project financing costs and policy incentives can significantly influence profitability.”
1. First Solar (NASDAQ: FSLR) — U.S. Manufacturing Strength
First Solar is among the largest U.S.-based solar module manufacturers. The company specialises in thin-film cadmium telluride (CdTe) technology rather than conventional crystalline silicon panels.
Recent earnings releases show a multi-year order backlog, reflecting sustained demand for utility-scale projects. Analysts attribute this to domestic manufacturing incentives and strong power purchase agreement pipelines.
The company’s technological differentiation offers some insulation from global silicon price volatility. However, it remains exposed to global competition and shifting trade policies.
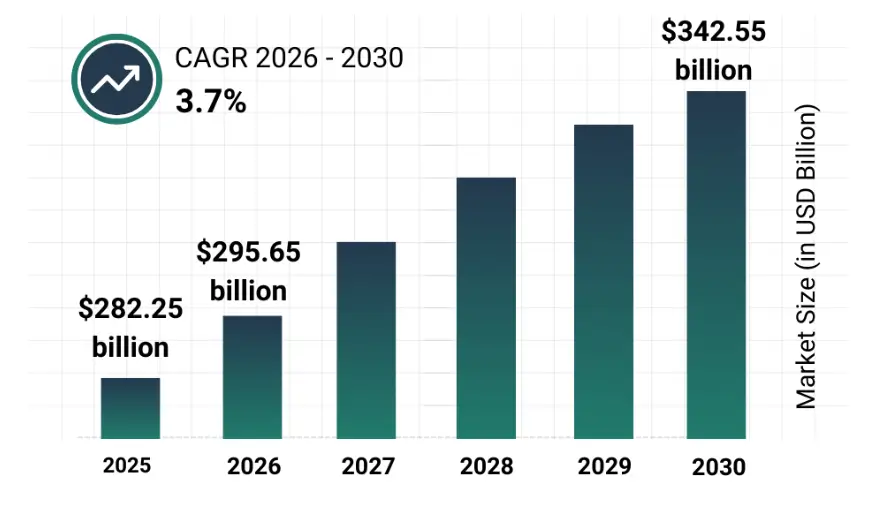
2. NextEra Energy (NYSE: NEE) — Renewable Utility Leader
NextEra Energy combines regulated utility operations with one of the world’s largest renewable energy development arms. Through NextEra Energy Resources, it operates extensive solar and battery storage capacity.
The company’s hybrid structure provides steady regulated revenues while expanding renewable growth. Analysts often cite its project pipeline and scale as key strengths.
Interest rate movements remain a factor, as utilities depend on debt markets to finance capital-intensive expansion.
3. Enphase Energy (NASDAQ: ENPH) — Solar Technology Innovator
Enphase Energy develops microinverters and energy management systems for residential and commercial solar installations. Unlike panel manufacturers, Enphase focuses on system-level optimisation and integration with storage.
The company has expanded into European and Australian markets. Analysts say distributed solar adoption trends support its long-term outlook.
However, residential solar demand is influenced by consumer financing conditions and housing market cycles.
4. Adani Green Energy Ltd. (NSE: ADANIGREEN) — Large-Scale Indian Renewable Expansion
India aims to reach 500 gigawatts of non-fossil capacity by 2030, according to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE). Adani Green Energy Ltd. has built one of the country’s largest renewable portfolios, primarily focused on solar and wind.
The company holds long-term power purchase agreements that provide revenue visibility. Analysts note its rapid capacity expansion aligns with national policy targets.
At the same time, high capital expenditure requirements and leverage levels require monitoring in a rising interest rate environment.
5. Tata Power Company Ltd. (NSE: TATAPOWER) — Diversified Energy with Solar Growth
Tata Power Company Ltd. combines thermal, hydro, and renewable generation assets, alongside a growing rooftop solar business.
Its diversified structure offers exposure across multiple energy segments. The company has invested in manufacturing and engineering capabilities, strengthening its position within India’s solar value chain.
Market observers note that Tata Power’s established infrastructure and operational experience differentiate it within India’s competitive energy landscape.
Additional Solar Names to Monitor
While the above five companies represent diverse solar segments, other firms frequently tracked by analysts include:
- Brookfield Renewable Partners (NYSE: BEP) — A global renewable asset operator with solar exposure.
- Canadian Solar (NASDAQ: CSIQ) — A major module manufacturer and project developer.
- Waaree Renewable Technologies (India) — A smaller-cap Indian solar manufacturer.
Investors often assess both pure-play manufacturers and diversified utilities when constructing clean energy portfolios.
Broader Sector Themes
Policy and Incentives (KW2)
Solar profitability is closely linked to tax credits, manufacturing subsidies, and renewable purchase obligations. In the U.S., domestic production incentives influence manufacturer margins. In India, auction frameworks and state-level targets drive deployment.
Policy continuity remains critical for sector stability.
Storage and Grid Integration (KW3)
Battery storage deployment is increasingly paired with solar projects. Firms investing in storage capabilities may benefit as grids transition toward round-the-clock renewable supply. Storage economics are improving, though capital requirements remain significant.
Capital Costs and Interest Rates (KW4)
Higher borrowing costs can affect project financing and equity valuations. Solar developers and utilities typically rely on long-term debt structures. Analysts therefore examine balance sheets and debt servicing capacity when evaluating renewable firms.
Valuation and Financial Metrics
Beyond sector trends, investors assess fundamentals including:
- Revenue growth
- Earnings stability
- Debt-to-equity ratios
- Return on invested capital
- Project backlog visibility
Solar manufacturers may exhibit higher volatility due to commodity price swings. Utilities often provide steadier earnings but slower growth.
“Clean energy is a structural theme, but stock selection requires financial discipline,” said a renewable sector strategist at a Mumbai-based brokerage firm.
ESG Investing and Institutional Flows
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) funds continue to allocate capital toward renewable sectors. Institutional mandates tied to climate risk disclosure frameworks have increased scrutiny of energy portfolios.
However, analysts note that ESG-driven flows can fluctuate depending on broader market sentiment and performance cycles.
Global Competition and Supply Chains
China remains the dominant global manufacturer of solar modules. Price competition from Chinese producers affects margins worldwide.
Companies outside China often compete through technological differentiation or domestic policy advantages. Trade policies and tariffs influence cross-border competitiveness. Supply chain diversification has become a strategic priority following pandemic-era disruptions.

Risks to Monitor
Solar stocks face multiple risks:
- Policy reversals or subsidy reductions
- Raw material price fluctuations
- Currency volatility
- Slower-than-expected project execution
- Regulatory challenges in emerging markets
Market analysts emphasise diversification and risk assessment within clean energy allocations.
Related Links
Gravity Battery: Generate Power by Dropping Weights; A Revolutionary New Energy Invention.
Solar energy remains central to the global clean energy transition. In 2026, companies such as First Solar, NextEra Energy, Enphase Energy, Adani Green Energy Ltd., and Tata Power Company Ltd. represent varied approaches to participating in that growth — from manufacturing and technology innovation to large-scale project development.
Each carries distinct opportunities and challenges. Investors evaluating Top 5 Solar Stocks opportunities must weigh macroeconomic conditions, regulatory frameworks, financial metrics, and long-term strategic positioning.
The renewable transformation continues to gather pace. Prudent analysis and diversification remain essential in navigating this evolving sector.









