India’s PM Surya Ghar Scheme, officially known as the Pradhan Mantri Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, has triggered a sharp rise in rooftop solar installations, with industry leaders reporting nearly 250% growth in residential solar adoption since the scheme’s launch in February 2024. As of early 2026, millions of households have installed rooftop systems.

The government has also introduced new February 2026 rules to streamline approvals, improve monitoring, and strengthen grid integration.
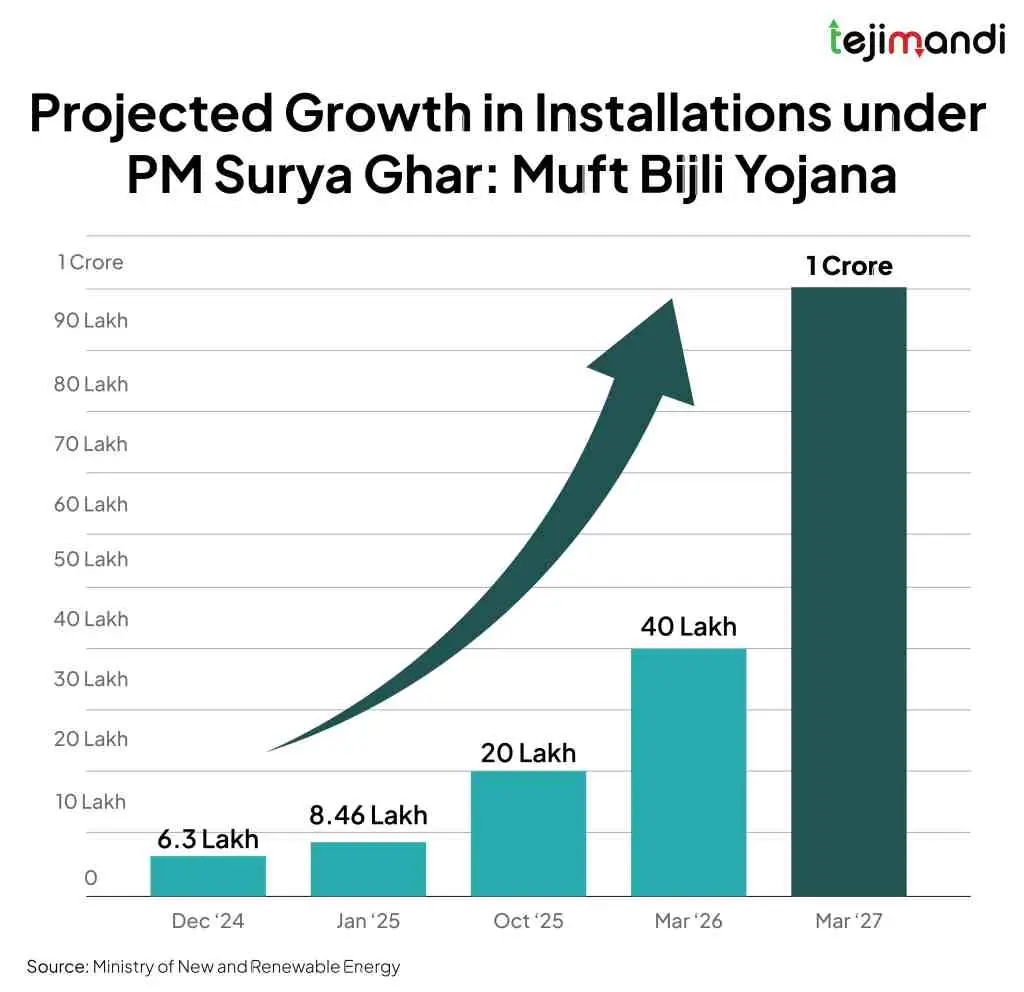
Record-Breaking Growth Under PM Surya Ghar Scheme
Surge in Installations
Since February 2024, the PM Surya Ghar Scheme has seen more than 20 lakh rooftop solar systems installed across the country. This surge, described by industry experts as a 250% increase, highlights the scheme’s effectiveness in overcoming barriers to solar adoption.
As reported by Mercom India, over 5 lakh households are now benefiting from subsidies and reduced energy bills. In December 2025, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) confirmed that subsidy disbursements had surpassed ₹14,000 crore, with 25 lakh households involved in the scheme.
Key Features of the PM Surya Ghar Scheme
Launched in February 2024, PM Surya Ghar was designed to:
- Install rooftop solar on 10 million households by 2027.
- Add 30 GW of distributed solar capacity.
- Provide 40% subsidies for residential systems and low-interest, collateral-free loans for eligible applicants.
These incentives, along with a digital application portal for ease of use, were expected to catalyse widespread adoption of residential solar.
Why Adoption Accelerated: Key Drivers
1. Financial Incentives and Accessibility
The scheme reduced the financial burden for low- and middle-income households by offering generous subsidies and low-interest loans. This has made rooftop solar systems much more affordable.
2. Simplified Digital Application Process
The introduction of the single-window national portal allowed users to apply for installation, track their subsidy status, and access vendors seamlessly. This digital transformation significantly sped up processing and approvals, which had previously been delayed due to bureaucratic inefficiencies.
3. Rising Energy Prices
As electricity tariffs have risen in several states, residential solar systems have become an attractive investment for households looking to reduce electricity bills. Solar power offers financial savings while contributing to India’s renewable energy targets.
February 2026 Rule Updates: What’s New
1. Unified Digital Approval Workflow
States and Union Territories must now adopt a standardised digital workflow for approvals, eliminating separate application charges and testing fees. This reform is aimed at reducing procedural barriers.
2. Real-Time Monitoring Mandate
The February 2026 regulations introduced real-time monitoring systems to track the performance of solar panels. These systems are designed to help utilities better manage grid integration and ensure that installations meet performance standards.
3. Net-Metering Harmonisation
Net-metering rules have been streamlined across states. Under the new guidelines, all installations must ensure compatibility with smart meters that allow for efficient energy export and real-time billing adjustments.
Regional Growth Patterns: Who Is Leading?
While Gujarat has led the way with nearly 4 lakh installations, Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh are also seeing significant growth. Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu follow closely behind, though adoption rates in Bihar and Odisha remain relatively low.
Regional disparities continue to be an issue, with more densely populated and industrial states adopting solar at a faster pace than rural or economically weaker areas.
Consumer Case Study: From Application to Installation
Ravi Kumar, a homeowner in Lucknow, applied for rooftop solar under PM Surya Ghar in early 2025. He received approval within 30 days and the installation was completed in 60 days.
“The process was smooth, and the subsidy was disbursed quickly. Our electricity bills have been slashed by over 70%,” says Kumar. His story reflects the growing ease of adoption under the scheme, but challenges remain for other consumers in states with slower regulatory responses.
Economic and Environmental Impact
Job Creation and Economic Stimulus
The solar value chain — from manufacturing to installation — has generated thousands of jobs, particularly in semi-urban and rural areas. Industry leaders estimate that rooftop solar adoption has directly or indirectly created more than 50,000 jobs in the past year alone.
Additionally, the rise in solar energy adoption has helped boost the Indian renewable energy market, pushing the country closer to its goal of achieving 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
Grid Resilience and Emission Reduction
The widespread adoption of rooftop solar also contributes to decentralised energy production, easing pressure on the central grid and reducing transmission losses. This is crucial for India’s energy resilience, especially in remote areas.
On the environmental side, the growth in solar capacity aligns with India’s climate change mitigation strategies. As of 2025, rooftop solar adoption alone has cut down nearly 5 million tonnes of CO2 emissions, contributing to India’s carbon-neutrality target by 2070.
Global Context: Lessons from Germany and Australia
India’s rooftop solar growth is on track with global benchmarks. Countries like Germany and Australia have seen rapid adoption through similar incentive schemes.
In Germany, the combination of feed-in tariffs and smart grid integration has driven residential solar uptake. Similarly, Australia’s combination of state and federal subsidies, along with incentives for battery storage, has encouraged solar installations on a large scale.
India’s adoption rate is competitive, though it lags behind in key areas like battery storage and consumer financing. Lessons from these countries could help India overcome remaining hurdles.
Challenges to Overcome: Remaining Barriers
While PM Surya Ghar has created momentum, several challenges remain:
Financing Access in Smaller Cities
Despite the availability of collateral-free loans, rural and semi-urban areas face barriers in accessing credit. Banks often require documentation or security, deterring many low- and middle-income consumers from adopting solar.
DISCOM Resistance
Despite strong growth, distribution companies (DISCOMs) in some states remain hesitant about rapid rooftop solar adoption due to concerns over lost revenue from reduced grid consumption.
Awareness Gaps in Rural Areas
While urban areas see high uptake, rural and remote communities still need more education on solar benefits and the financial savings it offers.

Related Links
Policy Recommendations for Scaling
To address these barriers, experts suggest:
- Targeted awareness campaigns for rural and semi-urban areas.
- Simplified credit access with government-backed loan guarantees.
- Incentivising DISCOMs through revised revenue-sharing models.
- Expanding battery storage solutions to enable energy independence.
The PM Surya Ghar Scheme has proven to be a game-changer for India’s renewable energy future, with 250% growth in rooftop solar adoption. While significant challenges remain, the scheme’s success demonstrates that with the right incentives, India can achieve its ambitious solar and renewable energy goals.
The February 2026 reforms are expected to further streamline adoption, enhance monitoring, and improve grid integration, ensuring that rooftop solar continues to be a cornerstone of India’s clean energy transition.








