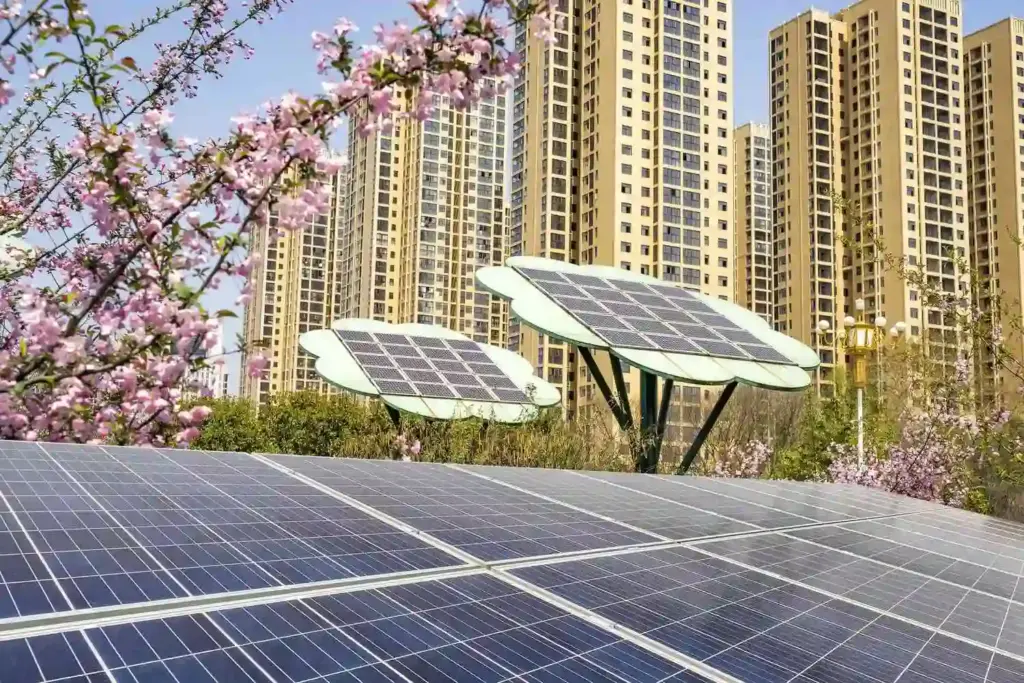
Solar Trees: High Power in Low Space; Smart ‘Solar Trees’ for Parks and Street are emerging as an innovative renewable energy solution for space-constrained urban areas.

Designed with vertically mounted photovoltaic panels arranged like branches, Solar Trees generate electricity for public lighting, charging infrastructure and smart city systems while occupying minimal land — addressing one of the key limitations of traditional solar deployment in dense cities.
What Are Solar Trees?
Solar Trees are engineered renewable energy structures that resemble natural trees. Instead of leaves, they support solar photovoltaic (PV) panels mounted on branching arms around a central trunk.
The concept draws inspiration from plant phyllotaxy — the arrangement of leaves in nature to maximise sunlight absorption. By staggering panel placement vertically and angularly, Solar Trees reduce self-shading and improve exposure across daylight hours.
Technically, Solar Trees operate like conventional solar PV systems:
- Sunlight hits PV cells.
- Electrons move within semiconductor materials.
- Direct current (DC) electricity is produced.
- An inverter converts DC into alternating current (AC).
The difference lies not in the energy principle, but in the spatial design.
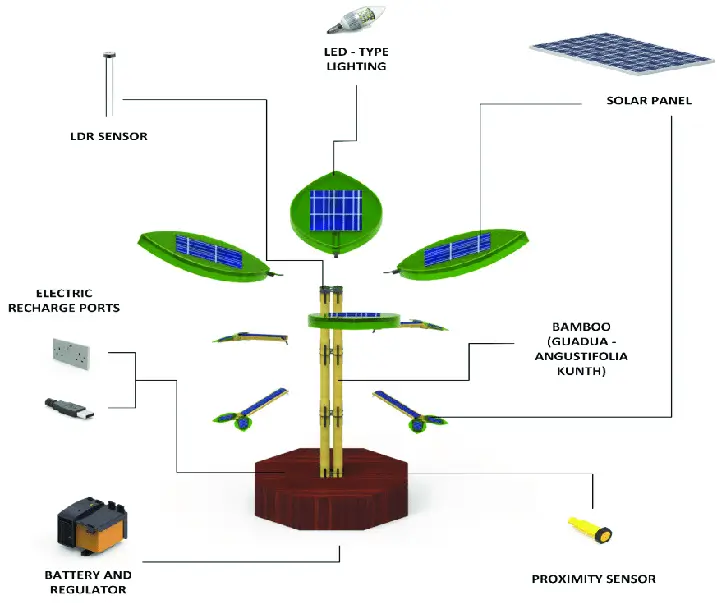
The Core Advantage: Land Efficiency
Land scarcity is one of the biggest barriers to solar expansion in urban areas. Traditional ground-mounted solar arrays require extensive horizontal space. Even rooftop installations depend on structural suitability, roof ownership and orientation.
Solar Trees reduce land footprint dramatically. A single installation may occupy as little as 3–5 square metres of ground space while generating several kilowatts of electricity. Urban energy planners view Solar Trees as particularly valuable in:
- Parks
- Road medians
- Pedestrian plazas
- Bus depots
- Railway stations
- Institutional campuses
In dense metropolitan environments, this vertical use of space is strategically significant.
Power Output and Performance Metrics
Solar Tree capacity depends on design and panel count.
Typical installations range between:
- 3 kW for smaller park installations
- 10–15 kW for municipal models
- 50 kW or more for clustered or institutional projects
India’s CSIR-CMERI developed a Solar Tree in West Bengal capable of generating over 50 kW while occupying significantly less land than a comparable flat array.
Energy analysts emphasise that Solar Trees are designed for distributed applications rather than grid-scale generation. However, when deployed in clusters across city zones, they can collectively contribute meaningful distributed power.
Integration with Smart City Infrastructure
Modern Solar Trees increasingly function as multifunctional public utilities.
Many installations integrate:
- LED lighting systems
- Electric vehicle (EV) charging stations
- USB charging ports
- Environmental monitoring sensors
- CCTV cameras
- Wi-Fi routers
- Digital display screens
This integration positions Solar Trees not only as energy generators but also as infrastructure nodes within smart city frameworks. Municipal authorities see value in combining renewable energy with digital connectivity and public amenities.
Case Studies: India and Abroad
India
Under various smart city initiatives, Solar Trees have been installed in:
- Public parks in Uttar Pradesh
- Government complexes in West Bengal
- Institutional campuses
Urban local bodies have cited reduced electricity bills and improved sustainability branding as benefits.
Europe and Southeast Asia
In Singapore, vertical solar installations have been incorporated into public gardens as part of sustainability showcases. In parts of Europe, Solar Trees have been installed in pedestrian areas to provide shaded seating and EV charging infrastructure.
These international examples demonstrate how Solar Trees can be adapted to different urban contexts.
Lifecycle Environmental Impact
Solar Trees produce zero operational emissions during electricity generation.
From a lifecycle perspective, emissions arise during:
- PV module manufacturing
- Steel structure fabrication
- Transportation
- Installation
However, lifecycle analyses of solar PV systems indicate that emissions are significantly lower than fossil fuel-based electricity over operational lifespans of 20–25 years.
By displacing grid electricity generated from coal or gas, Solar Trees contribute to cumulative carbon reduction.
Economic Analysis: Cost and Return
Upfront Investment
Solar Trees typically cost more than standard rooftop systems due to:
- Structural engineering
- Foundation requirements
- Smart integration components
- Design aesthetics
Installation costs vary widely depending on capacity and features.
Long-Term Benefits
Financial benefits may include:
- Reduced municipal electricity expenditure
- Revenue from EV charging
- Lower maintenance compared to diesel generators
- Branding and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) value
Energy economists note that Solar Trees should be evaluated on a multifunctional value basis rather than solely cost-per-kilowatt metrics.
Engineering and Safety Considerations
Solar Trees must meet structural safety codes.
Engineers must account for:
- Wind load resistance
- Seismic activity
- Corrosion protection
- Electrical grounding
- Public safety clearances
Because installations are located in public spaces, compliance with municipal engineering standards is critical. Regular maintenance schedules are necessary to ensure structural integrity and electrical safety.
Comparison with Alternative Urban Solar Models
| Feature | Solar Trees | Rooftop Solar | Solar Canopies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | Minimal | Roof-dependent | Parking area |
| Visibility | High | Low | Moderate |
| Capacity | Moderate | Moderate-High | Moderate |
| Smart Integration | High | Limited | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower | Moderate |
Solar Trees occupy a niche between aesthetic infrastructure and distributed renewable generation.
Challenges and Limitations
- Higher Initial Cost: Structural complexity increases capital expenditure.
- Limited Scalability: Not suitable for large-scale grid supply.
- Urban Shading Constraints: Surrounding buildings may affect performance.
- Maintenance Access: Elevated panels require specialised servicing.
Urban planners must evaluate these constraints carefully.
Manufacturing and Industrial Potential
India’s growing solar manufacturing base may support domestic production of Solar Tree components. If scaled effectively, Solar Trees could become an exportable urban renewable product for developing countries facing similar space constraints.
Industrial experts suggest that combining modular prefabrication with mass manufacturing could reduce costs over time.
Climate Resilience and Urban Adaptation
Solar Trees contribute to decentralised power resilience. In the event of grid disruptions, installations with battery storage can power:
- Emergency lighting
- Communication systems
- Critical public services
As climate-related disruptions increase, decentralised energy nodes may become more valuable in urban planning.

Outlook to 2030 and Beyond
Energy analysts suggest that Solar Trees will remain a supplementary but visible component of distributed renewable systems.
By 2030:
- Costs may decline with mass production.
- Smart integration may expand.
- EV charging integration may increase.
While they will not replace rooftop or utility solar, Solar Trees may become standard fixtures in high-visibility public spaces.
Related Links
Solar Trees combine renewable energy generation with intelligent urban design. By delivering electricity in minimal space, they address a central challenge of solar deployment in dense cities.
Although they carry higher upfront costs and limited scalability compared to traditional solar farms, their multifunctional utility — powering lighting, charging, digital infrastructure and public amenities — positions them as strategic components of decentralised clean energy systems.
As cities pursue sustainability targets and smarter infrastructure, Solar Trees may increasingly symbolise the integration of renewable power into everyday urban life.









