By 2026, the economics of electricity have shifted significantly, with rooftop solar now 40% cheaper than traditional coal-fired power in many regions. This price war, driven by advances in solar technology, falling costs, and growing grid competition, is reshaping the global energy landscape.

As fossil fuel prices remain volatile, solar’s growing affordability marks a pivotal moment in the transition to renewable energy.
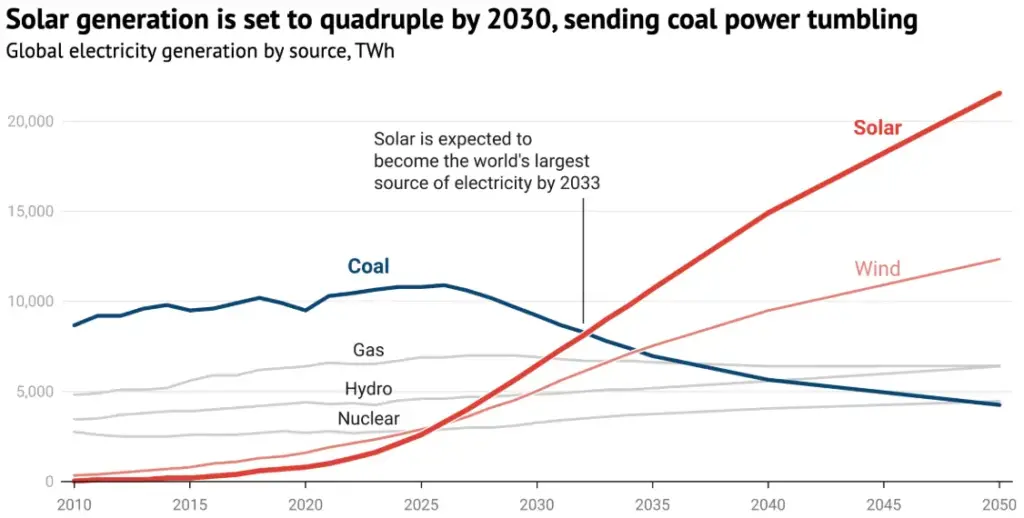
How Solar Is Beating Coal on Price
The energy sector is undergoing a dramatic transformation as solar power becomes increasingly affordable, thanks to technological advancements and scaling production. In contrast, coal, historically the dominant source of electricity generation, has faced rising operational costs and environmental pressures, leading to higher consumer prices.
The Cost of Electricity: A Changing Landscape
According to recent studies, the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) from rooftop solar has dropped dramatically in the last decade, now sitting at about $0.03 to $0.05 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) in many regions, depending on local conditions.
In comparison, traditional coal-fired electricity costs an average of $0.08 to $0.10 per kWh, with some areas reporting even higher prices due to factors like transportation and environmental regulations.
This price discrepancy is significant because it directly affects consumers’ energy bills. The average homeowner with a solar system is now paying far less for electricity than those relying on grid power, especially in areas with high coal dependency.
Factors Behind Solar’s Price Decline
Several factors have contributed to solar’s increasing cost-effectiveness:
- Decreasing Panel Prices: The cost of solar panels has fallen by nearly 90% since 2010, driven by advancements in manufacturing, economies of scale, and global supply chain improvements. (eia.gov)
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in photovoltaic (PV) technology, such as more efficient cell designs, have increased solar panel energy output, reducing the number of panels needed to generate the same amount of power.
- Improved Battery Storage: The cost of lithium-ion batteries, essential for storing solar energy, has also plummeted, enhancing the reliability and appeal of rooftop solar by allowing homeowners to store excess energy for use during non-sunny periods.
- Government Incentives: Many governments around the world have implemented subsidies, tax credits, and other incentives to make solar more affordable for consumers. In the U.S., for example, the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) has allowed homeowners to reduce the cost of solar installations by up to 26%.
- Declining Coal Costs: While coal costs have remained relatively high, operational costs have increased due to aging infrastructure, stricter emissions regulations, and volatile fuel prices. Coal is becoming increasingly expensive to mine, transport, and process, making it less competitive with renewable energy sources.
Coal’s Growing Financial Struggles
While solar prices continue to fall, coal is becoming more expensive. Several factors contribute to the rising cost of coal-fired electricity:
Fuel Costs: Coal prices are subject to volatility, with transportation and extraction costs often fluctuating. The global energy crisis, combined with trade disruptions, has pushed prices for coal even higher, contributing to increased electricity prices.
Carbon Pricing and Emission Controls: As countries pursue climate goals, many have introduced carbon pricing or cap-and-trade systems that make coal more expensive. These policies require coal-fired power plants to pay for the carbon emissions they produce, raising the operational costs of these plants.
Aging Infrastructure: Many coal plants around the world are aging, requiring costly maintenance and upgrades to meet modern environmental standards. The transition to cleaner energy sources makes investment in coal plants less appealing.
Public and Policy Pressure: Globally, governments and international organizations are tightening regulations on coal and other fossil fuels, which increases compliance costs. In many countries, there is also a growing political will to phase out coal in favor of greener alternatives.
The Role of Battery Storage in the Price War
One of the key drivers behind solar’s growing dominance is the increasing affordability and efficiency of battery storage technology. Solar power’s intermittent nature—generation peaks during the day and drops off at night—has been a barrier to its widespread adoption.
However, with the development of cost-effective battery systems, homeowners can store solar energy generated during the day and use it during evening hours when electricity demand and prices are highest.
Battery storage systems, which can cost anywhere from $5,000 to $15,000 depending on size and brand, have become increasingly common in solar installations.
This technology helps overcome solar power’s intermittency and maximizes the value of solar generation by enabling households to use stored power during peak demand times when coal-fired electricity is most expensive.
Moreover, as more households adopt solar-battery systems, virtual power plants (VPPs)—networks of connected homes that aggregate battery storage to supply power to the grid during peak demand periods—are emerging.
These systems enhance grid stability while enabling solar owners to earn additional income by selling stored energy back to the grid at premium rates during high-demand periods.
Environmental Costs and the Carbon Factor
While the economic price battle between solar and coal is critical, environmental factors play an equally significant role. The environmental costs associated with coal—including greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and ecosystem degradation—are rising sharply as global leaders work to meet climate targets outlined in the Paris Agreement.
Solar power, on the other hand, is a clean and sustainable energy source that produces no emissions during operation. In countries like New Zealand, which is aiming for net-zero emissions by 2050, the shift from coal to solar aligns with long-term climate goals and international obligations.
The rapidly declining cost of solar makes it easier for governments to implement carbon pricing schemes and encourage a faster transition to renewable energy. In terms of greenhouse gas emissions, coal is by far the worst offender.
Coal-fired power generation accounts for approximately 40% of global carbon emissions, making it one of the largest contributors to climate change. Solar power, in contrast, produces negligible emissions and is a key player in decarbonizing the global energy system.
Regional Variations and the Global Shift
The shift from coal to solar is not uniform across the globe. In regions with abundant sunlight and supportive policies, solar has already reached cost parity or is far cheaper than coal. For example:
- In parts of Australia, solar energy is already significantly cheaper than coal, with some regions experiencing as much as 50% cost savings for solar power compared to grid electricity prices.
- In the United States, states like California and Texas have seen a rapid expansion of solar, making it the cheapest form of new power generation. (npr.org)
- In developing nations, like India and Kenya, solar is being adopted rapidly due to its affordability, with solar power becoming competitive even without subsidies.
However, in coal-dependent countries such as China, India, and Poland, coal continues to dominate the energy mix, although growing economic and environmental pressures are gradually shifting the market toward solar energy in these regions as well.
What the 2026 Price Dynamics Mean for Consumers and Policy
The solar-coal price war has clear implications for consumers, policymakers, and the energy sector as a whole:
For Consumers: The cost advantage of solar will likely continue to grow, particularly as battery storage costs decrease and grid-connected solar installations expand. Homeowners can expect reduced energy bills and greater energy independence, particularly as renewable energy integration into national grids accelerates.
For Policymakers: Governments are increasingly incentivizing solar adoption to help meet carbon reduction goals and reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels. Policies such as feed-in tariffs and renewable energy standards are likely to expand, encouraging further growth in solar power.
For the Energy Sector: Coal companies will face continued pressure to innovate or transition to cleaner technologies. Meanwhile, solar companies and renewable energy developers are poised to benefit from increasing demand for clean energy solutions worldwide.

Related Links
A Clear Winner Emerging
The price war between coal and solar is well underway, and as of 2026, solar energy is clearly emerging as the cheaper, cleaner, and more reliable source of electricity for homeowners and grid operators alike.
This shift reflects broader trends in technology, economics, and environmental necessity, with solar power becoming an integral part of the global energy transition. As governments, consumers, and businesses continue to embrace solar, the battle between fossil fuels and renewable energy is tilting definitively toward a greener future.
FAQ
Q: Why is solar now cheaper than coal?
A: Solar has benefited from significant cost reductions in both panel production and battery storage technology, while coal remains burdened by fuel and environmental compliance costs.
Q: How do solar and battery systems help lower energy costs?
A: Solar panels generate free electricity from the sun, and batteries store excess energy for later use, reducing reliance on expensive grid power, especially during peak demand hours.
Q: Is solar power available everywhere?
A: Yes, while solar is most efficient in sunny regions, modern systems are capable of generating electricity in various climates, and battery storage ensures power is available when needed.









