Green Steel: Coal-Free Steel Production; Hydrogen Energy to Transform Heavy Industries is emerging as one of the most significant industrial shifts of the 21st century. By replacing coal in steelmaking with green hydrogen and renewable electricity, producers aim to cut emissions from one of the world’s most carbon-intensive sectors.

While pilot plants are operational, scaling remains complex, capital-intensive, and strategically important for energy security.
Why Green Steel Matters in the Climate Transition
Steel underpins modern economies. It is used in construction, transport, infrastructure, energy systems, and manufacturing.
Yet conventional steelmaking accounts for roughly 7–9% of global carbon dioxide emissions, according to estimates from the International Energy Agency (IEA). Most of these emissions come from blast furnaces that burn coal-derived coke to reduce iron ore.
In a traditional blast furnace:
- Iron ore (Fe₂O₃) reacts with carbon monoxide derived from coke.
- The chemical reaction releases carbon dioxide.
- Each tonne of steel produced emits approximately 1.8–2.2 tonnes of CO₂.
This heavy carbon footprint makes steel central to global decarbonisation efforts.
What Is Green Steel?
Green steel refers to steel produced with significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions than conventional methods.
There are three primary low-carbon pathways:
- Hydrogen-Based Direct Reduced Iron (H₂-DRI)
- Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) using recycled scrap
- Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) retrofits
Among these, hydrogen-based direct reduction has attracted global attention because it eliminates coal from the iron reduction process.
In hydrogen reduction:
- Hydrogen reacts with iron ore.
- The by-product is water vapour instead of carbon dioxide.
- The reduced iron is then melted in an electric arc furnace powered by renewable electricity.
If the hydrogen is produced using renewable power, the process can reduce emissions by up to 90–95%.
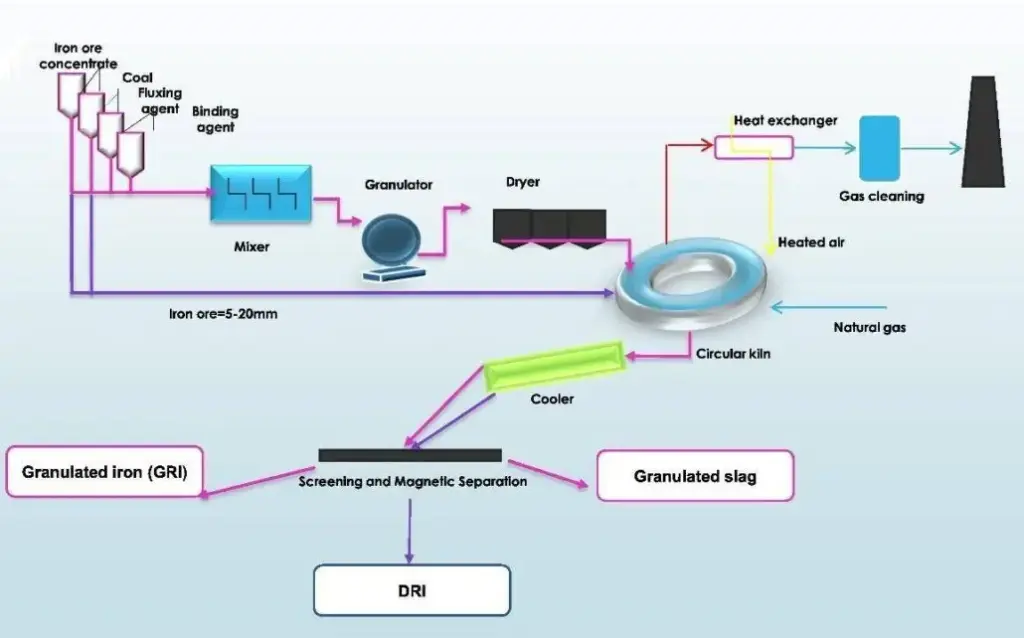
How Hydrogen Replaces Coal in Steelmaking
The core chemical difference lies in the reducing agent.
Blast Furnace Route:
Fe₂O₃ + CO → Fe + CO₂
Hydrogen Direct Reduction:
Fe₂O₃ + H₂ → Fe + H₂O
The hydrogen route avoids CO₂ formation at the reduction stage.
However, this process requires large volumes of hydrogen and substantial renewable electricity to produce that hydrogen through electrolysis.
According to industry modelling, producing one tonne of green steel may require approximately 50–60 kilograms of hydrogen. This translates into significant renewable electricity demand.
The Energy Demand Question
Hydrogen steel is energy-intensive. To produce green hydrogen, electrolysers split water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. If the electricity is renewable, the hydrogen is considered “green.”
Experts estimate that scaling hydrogen-based steel production globally would require massive expansion of renewable energy capacity.
For example, decarbonising Europe’s steel industry alone could require renewable electricity equivalent to the output of several large offshore wind farms. This energy demand is one of the largest structural challenges facing green steel.
India’s Strategic Position
India is the world’s second-largest steel producer and one of the fastest-growing. The government has launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission, targeting five million tonnes of green hydrogen production annually by 2030.
The Ministry of Steel has introduced a Green Steel roadmap encouraging pilot hydrogen-based DRI plants. Indian steel producers including Tata Steel, JSW Steel, and Jindal Stainless have announced hydrogen pilot projects.
An official from the Ministry of Steel recently stated that hydrogen steel could help India remain competitive under emerging global carbon regulations.
Global Industry Moves
In Sweden, the HYBRIT project led by SSAB has already produced fossil-free steel for commercial customers. Germany’s thyssenkrupp is building hydrogen-ready direct reduction facilities.
Australia, with its renewable resources and iron ore reserves, is exploring becoming a green iron exporter. China, the world’s largest steel producer, is experimenting with low-carbon pathways, though hydrogen adoption remains limited.
Economic Challenges: Can Green Steel Compete?
Hydrogen steel is currently more expensive than conventional production.Industry estimates suggest green steel may cost 20–40% more per tonne under present conditions.
Cost drivers include:
- Price of renewable electricity
- Electrolyser capital costs
- Hydrogen storage infrastructure
- Retrofitting or building new plants
However, analysts expect falling renewable costs and scaling electrolysers to reduce hydrogen prices over the next decade. Carbon pricing and border adjustment mechanisms may also narrow the cost gap.
Carbon Border Taxes and Trade Impact
The European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) will impose carbon costs on imported steel. This creates incentives for exporters, including India, to adopt low-carbon steel production.
Without decarbonisation, producers may face reduced competitiveness in carbon-regulated markets. Green steel could therefore become not only an environmental imperative but also a trade necessity.
Infrastructure and Financing Barriers
Transitioning to hydrogen steel requires:
- Gigawatt-scale renewable plants
- Electrolyser manufacturing capacity
- Hydrogen pipelines and storage
- Upgraded electric arc furnaces
Capital expenditure for converting a single integrated steel plant can run into billions of dollars. Financial institutions increasingly consider climate risk in lending decisions, influencing steel investment flows.
Public-private partnerships and blended finance may be required to de-risk early projects.
Employment and Just Transition
Coal-based steelmaking employs large workforces globally. Hydrogen-based processes may alter workforce requirements, emphasising digital operations, power systems, and hydrogen management. Governments must consider retraining programmes to ensure a just industrial transition.
Beyond Steel: Hydrogen in Heavy Industries
Hydrogen’s role extends beyond steel.
It is being explored in:
- Cement production
- Ammonia manufacturing
- Refining
- Shipping fuels
Heavy industries collectively represent a major share of global emissions. Green steel could serve as a blueprint for decarbonising other hard-to-abate sectors.

Certification and Standards
There is currently no universally accepted definition of “green steel.” Industry bodies and governments are working to develop emissions intensity benchmarks. Certification frameworks will be critical for buyers seeking low-carbon materials.
Timeline to 2050
Industry forecasts suggest:
- 2025–2030: Pilot and early commercial projects
- 2030–2040: Scaling of hydrogen DRI in regions with cheap renewables
- 2040–2050: Potential mainstream adoption if costs fall sufficiently
The pace will depend on policy alignment, infrastructure development, and technology cost curves.
Related Links
Solar Tiles: Replace Panels with ‘Solar Tiles’; Beautiful Roofs That Generate Free Power.
Flywheel Storage: Store Electricity Without Batteries! Understanding Flywheel Technology.
Green steel represents a transformative shift in how heavy industry operates. By replacing coal with hydrogen and renewable electricity, producers can dramatically cut carbon emissions in one of the world’s most polluting sectors.
Yet the path forward is capital-intensive and energy-demanding. Success will depend on falling hydrogen costs, supportive policies, and large-scale renewable deployment.
If achieved, coal-free steel production could redefine industrial competitiveness and accelerate global decarbonisation, positioning hydrogen energy at the centre of heavy industry’s future.









