India has taken a giant leap in its renewable energy journey with the successful launch of its first ocean wave energy project. Harnessing the power of sea waves, this groundbreaking project aims to provide clean, sustainable electricity to coastal cities.
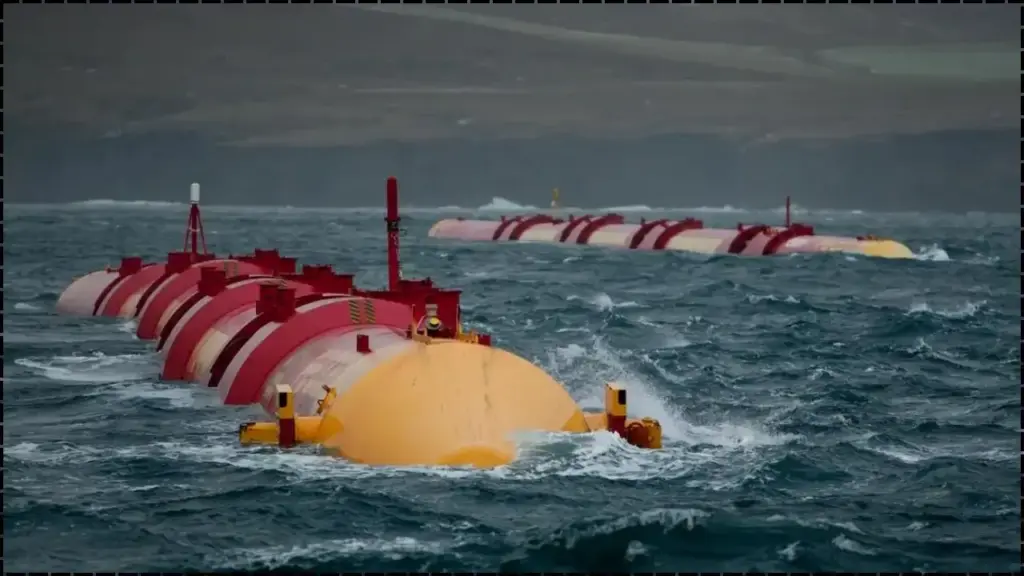

By tapping into the untapped potential of its coastline, India is on track to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and enhance energy security in coastal regions, providing a model for other countries to follow.
What is Ocean Wave Energy?
How Ocean Wave Energy Works
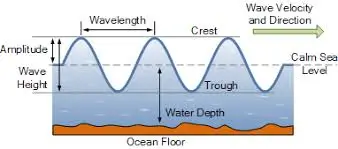
Ocean wave energy is one of the most promising forms of renewable energy, capturing the mechanical energy generated by ocean waves and converting it into electricity. Wave energy converters (WECs) are devices that float on the surface or are submerged underwater, where the motion of waves pushes or pulls mechanical systems, generating power through turbines, pistons, or hydraulic systems.
The energy produced from the waves can be harnessed both in shallow coastal areas and deeper offshore zones.
Given that waves are driven by wind, which is generated by consistent weather patterns, ocean wave energy provides a much more stable and continuous source of power than solar or wind energy.
India’s First Ocean Wave Energy Project
Project Overview and Location
India’s first ocean wave energy project is situated off the Tamil Nadu coast, a region identified for its high wave energy potential. The project uses point absorber technology, where floating platforms capture wave motion and convert it into electrical energy.
The initial installation has a modest generation capacity of 1 megawatt (MW), but it is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with plans to reach up to 100 MW by the 2030s.
This pilot project is not just a technical achievement but a crucial first step toward realizing India’s broader renewable energy goals. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has expressed its commitment to developing ocean energy technologies as part of India’s renewable energy strategy.
Government Support and Policy Framework
India’s ocean wave energy projects are supported by the government through the National Offshore Wind Energy Policy, which aims to harness offshore wind and wave energy potential along the country’s coastline.
The government is also exploring integrated ocean energy plans that can support renewable energy generation in coastal states, while ensuring minimal disruption to marine ecosystems.
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is actively working on regulatory frameworks to facilitate the development of ocean energy projects, offering incentives and subsidies for both private developers and research institutions. This is critical in ensuring that ocean wave energy can become a viable part of India’s renewable energy landscape.
Advantages of Ocean Wave Energy for India
1. Clean, Renewable Power
India’s transition to renewable energy is vital for reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. Wave energy is one of the cleanest sources of power, producing no greenhouse gases and requiring minimal land use, as the equipment is installed offshore. This makes it a sustainable, long-term solution for coastal cities.
2. Continuous Energy Supply
Unlike solar and wind, which are intermittent, ocean wave energy is available 24/7. The predictable nature of wave motion, driven by wind patterns, ensures a more stable energy supply.
This makes wave energy an ideal complement to other renewables like solar and wind, providing a reliable energy mix that supports grid stability and helps reduce reliance on conventional fossil fuels.
3. Reduced Dependency on Fossil Fuels
Wave energy is a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuel sources like coal and natural gas. By integrating wave energy into the national grid, India can reduce its dependence on fossil fuels, mitigating the negative environmental impacts associated with carbon emissions and air pollution.
This is a significant step toward achieving India’s renewable energy targets, which include generating 50% of electricity from non-fossil sources by 2030. (Source)
4. Supporting Energy Access for Remote Coastal Communities
In regions with limited access to the national grid, such as remote coastal towns or islands, ocean wave energy can provide a reliable and localized source of electricity.
This off-grid solution enhances energy access, improves the quality of life for coastal populations, and drives local economic development by powering homes, businesses, and essential services.
Challenges in Scaling Ocean Energy Projects
1. High Initial Investment
The installation of wave energy converters and associated infrastructure requires significant upfront capital investment.
The costs involved in building offshore platforms, connecting them to the grid, and maintaining the system are substantial. However, the long-term economic benefits of consistent, low-cost, clean energy can offset the initial costs over time.
2. Harsh Marine Conditions
The ocean is a challenging environment for infrastructure, with issues such as saltwater corrosion, extreme weather conditions, and biofouling (the accumulation of marine life on equipment). These challenges demand high durability in materials and regular maintenance to ensure the equipment remains functional over the long term.
To address these concerns, developers are working on advanced materials and maintenance protocols that can extend the life of the systems and reduce operating costs.
3. Grid Integration and Transmission
Ocean energy facilities require effective integration with the national grid. As the project grows, there will be a need for improved transmission infrastructure to carry power from offshore platforms to the mainland.
Effective energy storage solutions will also be necessary to manage the variability of wave energy and optimize energy distribution.
Comparison with Other Renewable Energy Sources in India
Solar and Wind Energy
While both solar and wind energy are growing rapidly in India, they still face challenges in terms of intermittency and space requirements.
Wave energy has the advantage of predictability, providing a consistent energy source regardless of time of day or season. Additionally, unlike solar and wind, wave energy requires minimal land use.
- Solar: A reliable source but intermittent; requires land and space.
- Wind: Intermittent, dependent on wind conditions, and needs significant land.
- Wave Energy: Consistent, 24/7, minimal land use, and complementary to solar and wind.
Each energy source has its own role to play, but combining them into a diverse energy mix will help India achieve energy security and sustainability goals.

Looking to the Future: Scaling Ocean Energy
Expansion and Future Projects
India’s first ocean wave energy project is just the beginning. As the technology matures, more projects are being planned along the country’s coastline, particularly in states like Maharashtra, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh, which have strong wave energy potential. These projects will expand India’s renewable energy capacity and further reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.
The government has committed to providing policy support, funding, and subsidies to encourage the growth of ocean energy. Over the next decade, it is anticipated that ocean energy could contribute a significant portion to India’s renewable energy targets.
India’s ocean wave energy project represents a bold step toward leveraging its maritime resources for sustainable power generation. By harnessing the motion of the sea, India is poised to provide clean, reliable electricity to coastal communities, reduce fossil fuel dependence, and meet its renewable energy goals.
While challenges remain in terms of cost and infrastructure, the future of ocean energy in India is promising, with technological advancements and government support driving the growth of this innovative energy source.









