In 2026, a growing number of New Zealand homeowners are shifting away from traditional grid power and adopting solar-battery systems to lower their energy bills, increase self-sufficiency, and contribute to the nation’s clean energy goals.

This shift is fueled by rising electricity prices, government incentives, and the growing efficiency of solar and storage technologies.
The Growing Appeal of Solar and Battery Systems
New Zealand, known for its abundant natural resources, has long been a global leader in renewable energy, with hydropower making up a large portion of its electricity supply. However, in recent years, solar energy has been gaining traction, particularly as a solution for homeowners looking to reduce energy costs.
By 2026, solar installations across the country have increased significantly, with more households opting for solar-battery combos rather than just relying on traditional power sources.
These systems, which pair photovoltaic (PV) solar panels with home batteries, are enabling Kiwis to generate and store their own electricity. Homeowners are no longer entirely dependent on the national grid, giving them more control over their energy consumption and financial savings.
Rising Energy Costs and Economic Factors
The high and rising cost of electricity in New Zealand has become one of the primary drivers of the shift toward solar power. According to a 2025 report from the Electricity Authority, residential electricity prices have increased by nearly 40% over the past five years, primarily due to infrastructure costs and increasing demand.
This has made many New Zealanders rethink their reliance on the grid, particularly when solar energy offers a viable alternative that can help cut costs.
Solar-battery systems allow homeowners to store excess energy produced during the day, using it later in the evening or during cloudy periods, significantly reducing their reliance on expensive grid power.
For example, if a household with solar panels produces more electricity than it uses during daylight hours, that excess energy can be stored in a battery and used later at night when electricity demand and prices are higher.
This kind of energy independence is increasingly attractive to homeowners, who can save hundreds of dollars per year by using solar-generated power instead of grid electricity.
The Technological Push: Solar and Batteries Becoming More Efficient
Another key factor driving the adoption of solar-battery systems is the advancement in technology. Solar panels are now far more efficient than in years past, meaning homeowners can produce more energy from the same amount of roof space.
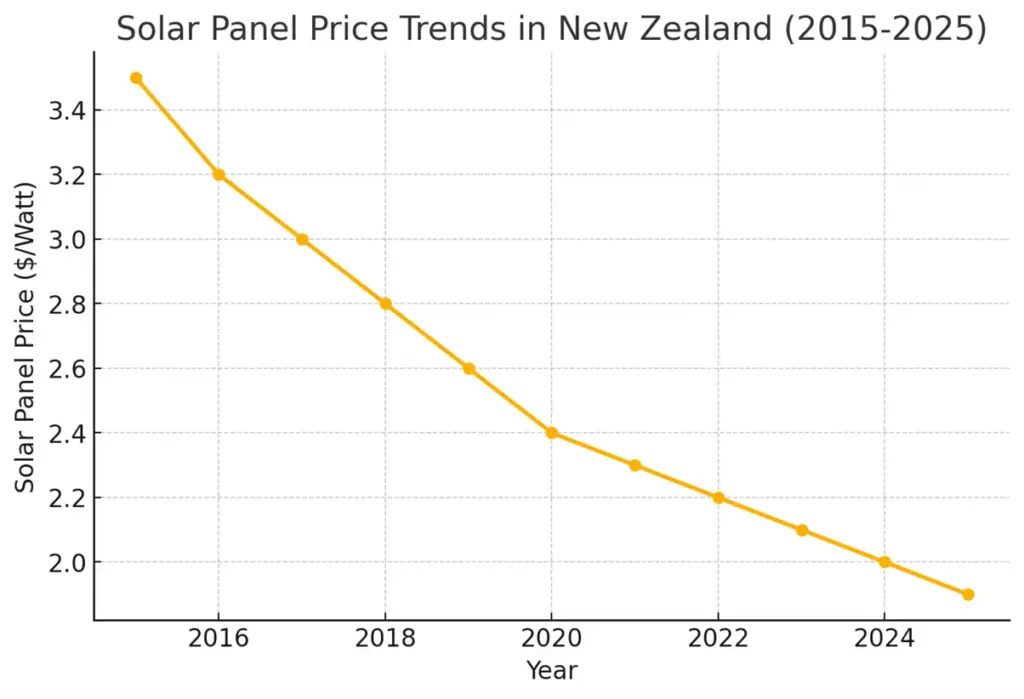
Additionally, battery storage technology has improved, becoming both more affordable and more reliable. In 2026, the average cost of a solar-battery combo in New Zealand has fallen by approximately 30% compared to five years ago.
This decrease is attributed to improvements in battery chemistry, more widespread availability of components, and increased competition in the solar energy market.
Manufacturers such as Tesla and SolarEdge have significantly reduced the prices of their solar batteries, making it more accessible to homeowners. These developments have allowed many more Kiwis to install these systems and take advantage of the economic benefits.
Government Support and Incentives
Government policies have also played a critical role in encouraging homeowners to adopt solar and battery systems. New Zealand’s government has introduced several incentives to help families reduce the upfront cost of installing these systems.
One of the most significant initiatives is the Clean Energy Investment Subsidy, which provides rebates for the installation of solar panels and home batteries. The program was launched in 2025 to meet New Zealand’s climate goals and is expected to cover up to 30% of the cost of installation, depending on household income.
The government’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 has further strengthened these incentives, making it easier for New Zealand homeowners to transition to sustainable energy sources. These rebates, combined with the falling costs of solar technology, are making it financially feasible for many to make the switch.
Energy Independence and Grid Stability
Another reason for the growing popularity of solar and battery systems is the increased desire for energy independence. Aotearoa has witnessed extreme weather events in recent years, from flooding to power outages caused by storms.
These events have highlighted the vulnerability of centralized energy systems and the need for greater resilience. With solar-battery systems, homeowners are less reliant on the national grid during emergencies. Battery storage can provide essential backup power during blackouts, allowing families to keep the lights on, charge devices, and power key appliances.
As climate change increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, this resilience is becoming a critical factor for many households.
Grid Impact and the Rise of Virtual Power Plants
The growing trend toward solar and battery systems is not just about personal savings; it also has broader implications for the country’s energy grid. As more households generate and store their own power, less electricity is required from the central grid, which can help alleviate pressure during peak demand times.
In fact, the excess energy generated by solar homes can be exported back into the grid, helping to stabilize supply during periods of high demand. Some utilities are already starting to incorporate these distributed energy systems into larger virtual power plants (VPPs).
In a VPP, solar and battery systems from multiple homes are connected and coordinated to supply power to the grid when needed, acting like a small-scale power plant. This can help reduce the need for fossil fuel-based backup generation, further supporting New Zealand’s transition to a low-carbon economy.
The Environmental Benefits of Solar Power
The environmental benefits of solar energy are another driving factor for homeowners choosing solar and batteries. New Zealand has long been a global leader in renewable energy, with around 85% of its electricity already coming from renewable sources such as hydropower and wind.
However, to meet the government’s ambitious carbon neutrality goals by 2050, the country must significantly increase its use of solar energy.
Households with solar-battery systems help reduce the overall carbon footprint of the country. By generating their own renewable power, these homeowners contribute to the national goal of reducing dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Solar power, paired with battery storage, is considered one of the most effective ways to achieve energy self-sufficiency while minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.
It helps reduce reliance on grid energy, particularly during times of high demand when non-renewable sources like coal and natural gas are often used to meet the shortfall.
What Are the Challenges to Widespread Adoption?
While the benefits are clear, there are still barriers to widespread solar adoption in New Zealand. The initial capital cost of installing solar panels and batteries remains a significant obstacle for many homeowners, particularly for those in rental properties or lower-income brackets.
Although government incentives have helped reduce costs, the upfront investment is still a challenge for some. Additionally, although solar panel efficiency has improved, it still doesn’t provide a consistent energy supply, particularly during periods of low sunlight or in the winter months.
Batteries offer a solution, but even modern batteries can only store a limited amount of power, meaning that solar homes are still reliant on the grid during certain times.
Despite these challenges, industry experts predict that as technology advances and costs continue to fall, solar-battery systems will become more affordable and accessible to a wider range of Kiwis.

What’s Next for Solar and Battery Solutions in New Zealand?
Looking ahead, experts believe that New Zealand is on track to dramatically increase the role of solar energy in its electricity mix. By 2030, solar-battery systems are projected to provide a significant portion of the country’s power needs, alongside other renewable sources like wind and hydroelectricity.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more efficient panels, longer-lasting batteries, and smarter grid systems that allow for better integration of decentralized power.
Further government incentives and financial support could also play a crucial role in making these systems accessible to more homeowners, helping New Zealand achieve its clean energy goals.
Related Links
A Brighter, Greener Future
In 2026, New Zealand homeowners are increasingly choosing solar-battery systems to take control of their energy use, save money, and contribute to the country’s ambitious sustainability goals.
With technological advancements, government incentives, and the growing desire for energy independence, the solar shift is likely to accelerate in the coming years. As more Kiwis embrace clean, renewable energy solutions, New Zealand will move closer to its vision of a low-carbon, self-sufficient energy future.
FAQs
Q: How much can I save by installing solar panels and a battery?
A: Homeowners can save anywhere from 30% to 70% on their electricity bills depending on their system size, energy consumption, and solar generation.
Q: Are there incentives for installing solar panels in New Zealand?
A: Yes, the Clean Energy Investment Subsidy provides rebates for solar panel and battery system installations, covering up to 30% of the installation cost.
Q: What happens if my solar panels produce more energy than I need?
A: Excess energy can be exported back to the grid for a credit or stored in a battery for later use.









