Perovskite Cells are rapidly advancing from laboratory innovation to early commercial production, positioning themselves as a potential successor to traditional silicon solar panels. With record-breaking efficiency levels and lower projected manufacturing costs, perovskite technology could reshape global solar deployment.
Yet experts caution that durability, environmental safety and large-scale bankability remain decisive hurdles before widespread adoption.
What Are Perovskite Cells?
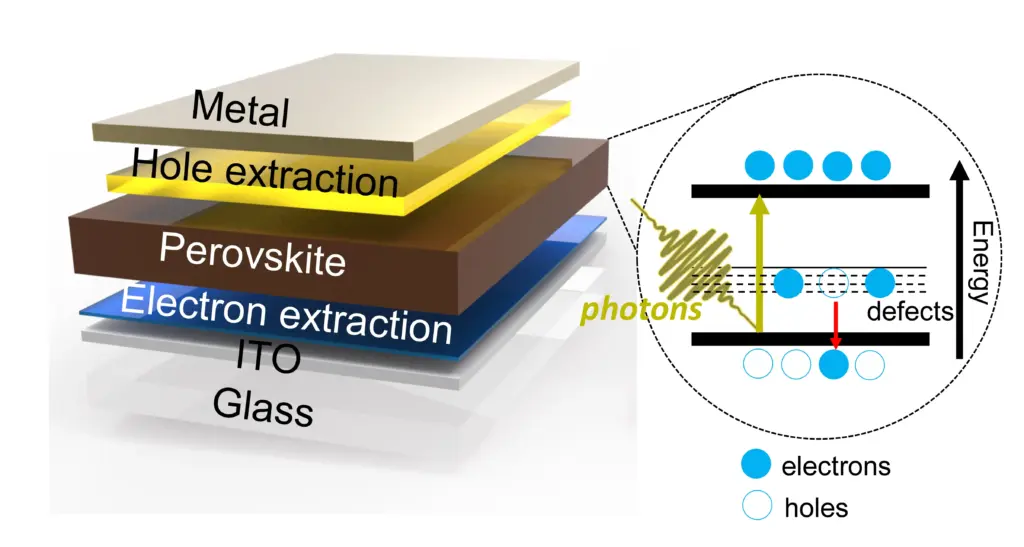
Perovskite Cells are photovoltaic devices built using perovskite-structured materials, typically hybrid organic-inorganic compounds containing lead or tin halides. These materials efficiently absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity.
Unlike crystalline silicon wafers, perovskites can be manufactured as thin films using lower-temperature processes. This enables lightweight, flexible solar modules and potentially lower capital expenditure in production facilities.
According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), laboratory efficiency of perovskite solar cells has risen from below 4 per cent in 2009 to over 25 per cent in certified single-junction cells today. This represents one of the fastest efficiency improvements in photovoltaic research history.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes in its renewable energy outlook that solar remains the fastest-growing power generation technology globally. However, conventional silicon cells are approaching their theoretical efficiency ceiling.
Efficiency Records and Tandem Breakthroughs
A major development involves tandem solar cells, where a perovskite layer is stacked atop a silicon cell. This configuration allows each material to absorb different parts of the solar spectrum.
Recent research collaborations have reported tandem efficiencies exceeding 33 per cent under controlled laboratory conditions. Oxford PV has announced commercial-scale modules achieving efficiencies above 26 per cent, higher than most conventional rooftop panels currently sold.
Professor Henry Snaith, co-founder of Oxford PV and physicist at the University of Oxford, has publicly stated that tandem designs “unlock performance beyond the single-junction silicon limit.”
Higher efficiency means more electricity generation per square metre, reducing land requirements and increasing rooftop output.
Manufacturing Advantages and Industrial Transition
Silicon solar manufacturing requires high-temperature furnaces exceeding 1,000 degrees Celsius, contributing to high energy consumption in production.
Perovskite films can be deposited at temperatures below 200 degrees Celsius using solution processing, inkjet printing or vapour deposition. These techniques may allow roll-to-roll manufacturing similar to newspaper printing.
According to cost modelling studies published in peer-reviewed energy journals, perovskite module production could fall below $0.60 per watt if scaled successfully.
Dr. Laura Schelhas, formerly of NREL, has written that simplified manufacturing “could significantly lower barriers to entry for new solar manufacturing hubs.”
However, silicon manufacturing costs have declined sharply over the past decade due to global scale, especially in China. Competing with that established supply chain presents a major challenge.
Supply Chain and Geopolitical Implications
Today’s silicon solar supply chain is heavily concentrated in East Asia. This concentration has prompted strategic policy responses in the United States, European Union and India.
Perovskite production may diversify supply chains because it relies on different materials and simpler processing equipment.
The European Commission, in its Net-Zero Industry Act discussions, has emphasised the need to strengthen domestic clean energy manufacturing capacity. Advanced photovoltaic technologies are seen as part of that strategy.
However, perovskite materials often contain lead. Ensuring safe sourcing, handling and recycling will be essential to avoid new environmental dependencies.
Durability and Stability: The Core Technical Risk
Durability remains the most critical unresolved issue for Perovskite Cells. Perovskite materials are sensitive to moisture, oxygen and heat. Silicon panels typically carry 25-year warranties. Investors expect similar performance for new technologies.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has reported significant progress in improving encapsulation methods and material formulations. Accelerated stress tests now show multi-thousand-hour stability under laboratory conditions.
Dr. Joseph Berry, senior scientist at NREL, has stated in technical briefings that stability has improved “by orders of magnitude,” but long-term outdoor field data is still being accumulated.
Environmental and Recycling Considerations
Environmental groups have raised concerns regarding lead content in many high-efficiency perovskite cells. Researchers argue that the amount of lead in a module is relatively small and encapsulated. However, end-of-life recycling frameworks must be established to prevent leakage.
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) has emphasised in reports on photovoltaic waste management that recycling systems must scale alongside solar deployment to prevent environmental risk.
Lead-free tin-based perovskites are under active research, though they currently exhibit lower efficiency and stability.
Bankability and Investor Confidence
Even if efficiency and cost targets are achieved, large-scale solar deployment depends on bankability. Infrastructure investors require long-term performance data before financing gigawatt-scale projects. Silicon benefits from decades of field validation.
Professor Martin Green, a photovoltaic researcher at the University of New South Wales, has observed in industry forums that tandem technologies represent a “logical next phase,” but must demonstrate consistent performance in diverse climates.
Insurance providers will also assess degradation risk before underwriting projects involving Perovskite Cells.
Building-Integrated and Urban Applications
Perovskite’s lightweight and semi-transparent properties enable building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). These modules can be incorporated into facades, windows and urban infrastructure where conventional silicon panels may be impractical.
Urban deployment could expand solar generation without additional land use, particularly in densely populated regions.
Implications for India
India continues expanding solar capacity under national renewable energy targets. Nearly all installed capacity currently uses crystalline silicon modules. Domestic research institutions, including the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) system, are conducting advanced studies on perovskite materials.
If durability improves, perovskite-silicon tandems could increase output from rooftop installations in Indian cities, where space constraints limit capacity.
However, experts note that India would need to develop material supply chains, certification standards and recycling frameworks before large-scale adoption.
Climate and Grid Impact
Higher efficiency modules reduce land use and balance-of-system costs. They also lower the levelised cost of electricity over time. The United Nations (UN) and IRENA have highlighted that renewable capacity must expand rapidly to meet global climate targets.
Perovskite technology could contribute to this expansion by improving output density and enabling novel installation formats.
However, grid integration challenges remain independent of module technology. Transmission infrastructure, storage capacity and grid management systems must expand in parallel.
Balanced Outlook: Complement or Replacement?
Experts caution against framing perovskite as an immediate replacement for silicon. Silicon technology benefits from global scale, falling costs and proven reliability. Tandem approaches combining silicon and perovskite may represent the most realistic near-term path.
BloombergNEF analysts have noted that early adoption may occur in premium rooftop markets before scaling to utility-scale projects. Industry observers expect gradual integration rather than abrupt displacement.
Related Links
Energy from the Stars? How Space-Based Solar Panels Could Solve Earth’s Power Crisis.
No More Plug-ins? New Wireless Tech Will Charge Your Electric Car While You Drive!
Over the next five to ten years, field data will determine whether Perovskite Cells achieve bankable lifetimes. Manufacturers are scaling pilot lines. Governments are offering clean energy incentives. Researchers continue improving stability and material formulations.
If durability and environmental safeguards meet commercial standards, perovskite technology could redefine photovoltaic performance benchmarks.
Perovskite cells represent one of the most promising advances in solar power in recent decades. Rapid efficiency gains, lower-temperature manufacturing and tandem compatibility position them as a credible successor or complement to silicon photovoltaics.
Yet large-scale deployment depends on solving durability, recycling and bankability challenges. As the global energy transition accelerates, perovskite technology stands at a pivotal moment between scientific breakthrough and industrial transformation.









