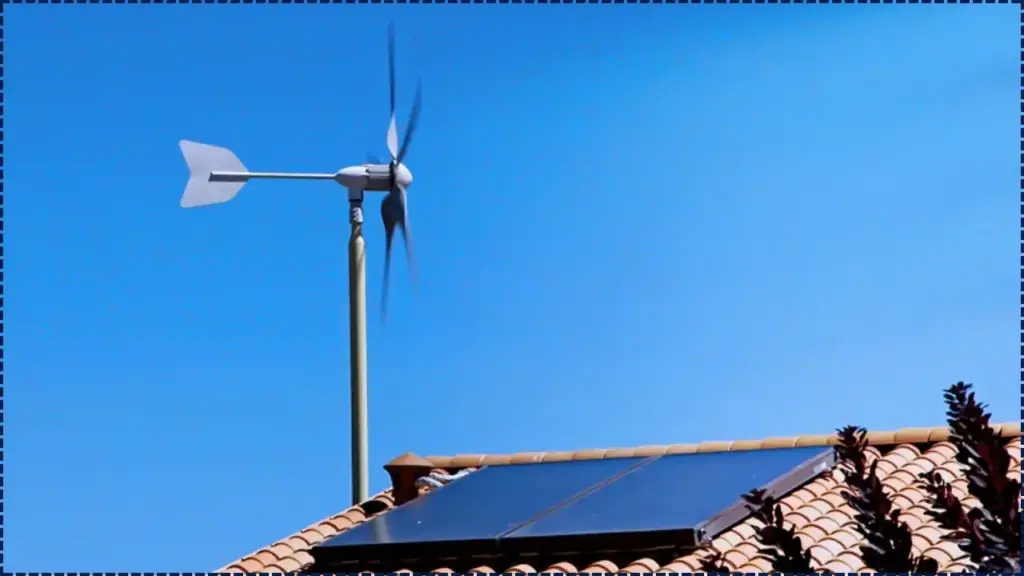
As the world seeks cleaner, more sustainable energy sources, portable rooftop wind turbines are emerging as a potential game-changer in residential power generation. These compact turbines, designed to be easily installed on rooftops or in small spaces, promise to provide renewable electricity even in low-wind environments.

But how do these wind turbines compare to solar power? Are they a better option for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint, or will solar panels remain the go-to solution for residential clean energy?
In this article, we explore the benefits and drawbacks of portable wind turbines, assess their potential for widespread adoption, and determine if wind energy can truly compete with solar power for everyday household use.
Introduction: Wind Power for Every Roof
Portable wind turbines are being hailed as an innovative solution for households seeking to generate clean energy directly from their rooftops. These turbines promise to harness the power of the wind, even in urban areas with limited space and inconsistent wind patterns, potentially turning any home into a self-sufficient energy producer.
But can these turbines truly compete with the more widely adopted solar panels? While both technologies aim to provide renewable electricity, they come with their own sets of challenges and advantages.
This article dives into the technology, cost, practicality, and efficiency of small wind turbines compared to solar panels, offering a balanced perspective on which renewable energy solution is best suited for different needs.
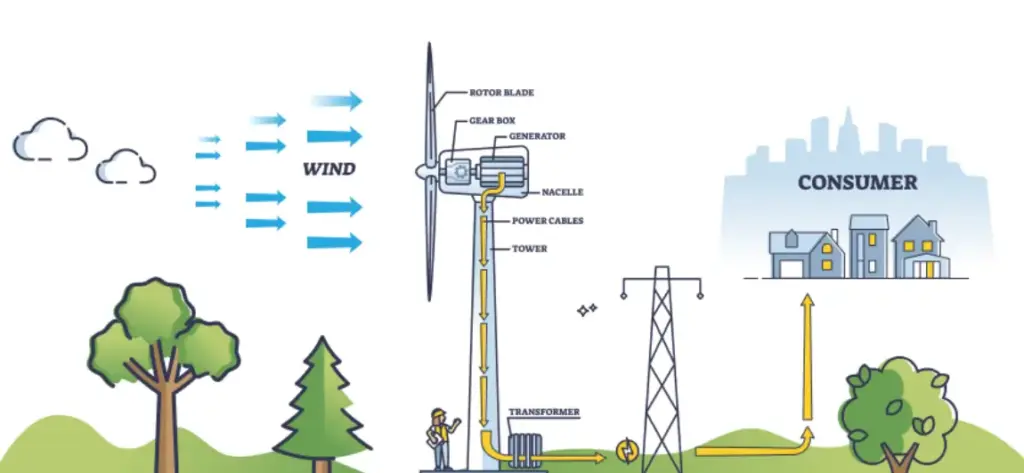
How Do Portable Wind Turbines Work?
Wind Turbine Basics
Portable wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity using blades or rotors that spin as wind passes over them. These turbines can be divided into two categories: horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWTs) and vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWTs).
- Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs): These turbines are the most common and have blades that spin on a horizontal axis, similar to the large-scale turbines used in wind farms. They typically require higher wind speeds to generate significant power.
- Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs): These turbines have blades that spin on a vertical axis and can operate in a wider range of wind directions, making them more suitable for urban environments and rooftops where wind is unpredictable.
Compact Design for Rooftop Installation
Unlike large-scale wind turbines, portable wind turbines are designed for smaller spaces, typically mounted on rooftops or balconies. Their compact design allows them to generate electricity without requiring significant land area.
These turbines work by capturing the kinetic energy from the wind and converting it into electricity, which can then be stored in batteries or fed into the home’s electrical grid.
Some portable wind turbines use a direct current (DC) generator, which is ideal for battery charging and off-grid systems, while others may use an alternating current (AC) generator for use in grid-tied applications.
Wind Power vs. Solar Power: Which is Better for Your Roof?
While both wind power and solar power are considered clean, renewable energy sources, they have different benefits and limitations. Here’s a breakdown of how each system works in residential settings:
1. Energy Generation and Efficiency
- Solar Power: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. They are most effective in sunny climates and can generate power even on cloudy days. Solar panels have an average efficiency of 15%–22%, meaning they convert that percentage of sunlight into usable energy. Solar systems typically generate consistent power during daylight hours and are best suited for areas with regular sunlight.
- Wind Power: Wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity by spinning blades that turn a generator. Their efficiency is highly dependent on local wind conditions. In windy regions, turbines can generate significant amounts of power. Small wind turbines typically operate at around 35%–45% efficiency, which is higher than solar in areas with consistent wind.
2. Location and Space Requirements
- Solar Power: Solar panels can be installed on roofs or open land and require minimal maintenance. In urban areas, rooftop solar panels are common because they utilize available space without occupying land. Solar power requires direct sunlight, so it is most effective in regions with ample sunlight year-round.
- Wind Power: Wind turbines need to be installed in areas with consistent and strong winds. This can be a challenge for urban rooftops, where wind patterns can be turbulent and inconsistent. Vertical-axis wind turbines are better suited for residential areas because they can operate in multiple wind directions and low wind speeds. However, the efficiency still depends heavily on local wind conditions.
3. Cost of Installation and Maintenance
- Solar Power: The cost of solar panels has decreased significantly over the past decade. On average, the cost to install a solar system is around ₹45,000–₹70,000 per kilowatt in India, with additional costs for inverters and battery storage. Maintenance costs for solar are relatively low, as they have no moving parts.
- Wind Power: The cost of portable wind turbines is typically higher per watt than solar panels, especially for small-scale residential units. A small wind turbine can cost anywhere from ₹70,000–₹150,000 depending on the model and power output. Additionally, wind turbines require more maintenance because of the moving parts, such as blades and gears, which need periodic servicing.
Challenges Facing Portable Wind Turbines
1. Wind Availability
One of the biggest limitations of residential wind turbines is the need for strong, consistent wind. Many homes, particularly in urban areas, do not experience sufficient wind speeds to make wind turbines efficient.
Turbulent wind caused by surrounding buildings or trees can reduce turbine efficiency. Even the best-designed turbines can struggle to produce power if wind speeds are low or inconsistent.
By contrast, solar panels can generate power anytime sunlight is available, regardless of local wind conditions, making them a more predictable energy source.
2. Noise and Aesthetics
Traditional wind turbines can produce significant noise, especially at higher speeds. Although smaller turbines are quieter, some homeowners may still find the whirring of blades intrusive.
Additionally, the appearance of wind turbines may not always blend with the aesthetics of a residential property. However, vertical-axis turbines are generally quieter and may be a better choice for residential areas with noise concerns.
3. Efficiency in Urban Settings
Urban areas, with their tall buildings, narrow streets, and low wind speeds, are typically less favorable for wind turbines. In contrast, solar panels work well in these environments, as long as there is sufficient sunlight.
Even in cities with moderate sunlight, solar panels are more likely to produce reliable power than wind turbines, which depend on unpredictable wind patterns.
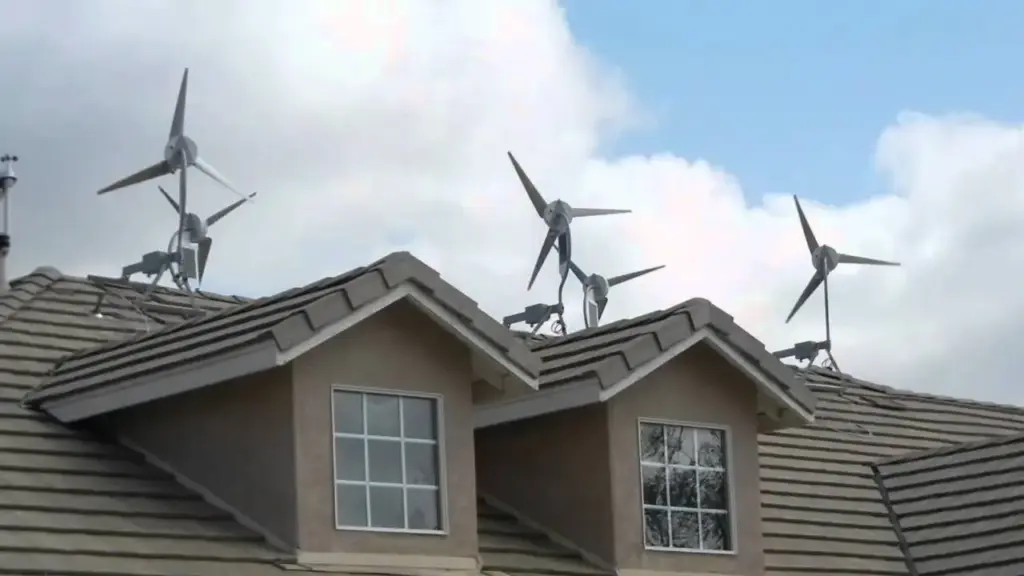

Real-World Applications and Pilot Projects
1. India’s Rooftop Wind-Solar Hybrids
In India, there have been efforts to integrate small wind turbines with solar systems in urban settings. In places like Gujarat and Rajasthan, projects have combined both solar and wind energy to harness dual renewable sources for residential use. These hybrid systems have been successful in areas with inconsistent sunlight but high wind speeds.
2. Vertical-Axis Turbines in Europe and the U.S.
In Europe and the United States, companies have been experimenting with vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWTs) for urban use. These turbines are smaller, quieter, and can capture wind from multiple directions.
While these systems have shown promise in low wind conditions, they are still not as widespread as solar systems, and the cost-to-benefit ratio remains an area of active research.
Related Links
Your House Walls Could Soon Generate Electricity! Meet the Bio-Panels Made of Algae.
Forget Lithium-Ion! This New Graphene Battery Charges Your EV in Just 120 Seconds.
Solar vs. Wind – The Best Option for Residential Use
While portable wind turbines offer a promising alternative to solar power, they are currently not as efficient or reliable for most residential settings. Solar panels, with their consistent performance, lower maintenance costs, and better suitability for urban rooftops, remain the most practical and cost-effective renewable energy source for most homeowners.
That being said, wind turbines could play a valuable complementary role in locations with strong and consistent winds, or as part of a hybrid renewable system that combines solar and wind power to ensure round-the-clock energy production.
For homes in low-wind urban areas, solar power remains the better option, but in more wind-prone areas, small wind turbines could supplement or even replace solar systems in the future, especially with innovations like bladeless designs and improved vertical-axis turbines.
The key to the future of home energy lies in understanding local resources and combining the strengths of both wind and solar to create sustainable, reliable, and cost-effective energy systems for every roof.









