As Earth faces an escalating energy crisis, space-based solar panels (SBSP) have emerged as a promising solution. These panels, orbiting the planet, could harvest sunlight without interference from the atmosphere and beam energy back to Earth.

While still in early development stages, experts believe space solar power may one day offer continuous, clean energy, potentially solving global power shortages and addressing climate change.
What is Space-Based Solar Power?
The Concept of Solar Power from Orbit
Space-based solar power (SBSP) refers to the idea of placing solar panels or satellites in orbit around Earth to capture sunlight and transmit it wirelessly back to the surface. Unlike traditional solar power, which is affected by weather conditions, nighttime, and seasons, space-based systems would be able to collect energy continuously, 24/7.
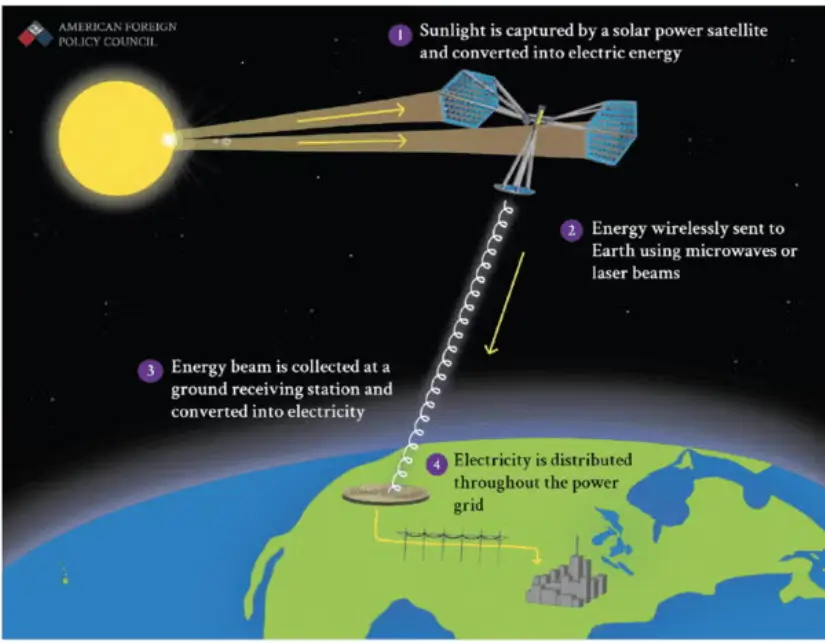
The process of SBSP involves several key components:
- Energy Collection: Large solar arrays capture sunlight in space.
- Energy Conversion: The sunlight is converted into microwaves or laser beams.
- Energy Transmission: The energy is transmitted to Earth, where it is received by large rectennas (rectifying antennas), which convert the energy back into usable electricity.
SBSP could allow for a reliable, unbroken flow of energy without being affected by terrestrial disruptions, providing a robust solution to energy needs around the world.
How Does Space-Based Solar Power Work?
A Complex Yet Feasible Technology
The concept behind SBSP is straightforward: gather solar energy in space where it’s not obstructed by the Earth’s atmosphere and then transmit that energy back to Earth. However, to make this a reality, several technologies must be developed and perfected.
- Energy Collection: Solar panels would be mounted on satellites or large space structures that would orbit Earth, positioned at geostationary orbits about 36,000 km above the planet. In this orbit, the panels would experience constant sunlight and could generate energy much more efficiently than on Earth’s surface.
- Energy Conversion: The collected solar energy would be converted into microwaves or lasers. These are forms of electromagnetic radiation that can be transmitted through space without being obstructed by the atmosphere, unlike light energy.
- Energy Transmission: The microwaves or laser beams would be directed towards Earth, where large rectennas on the ground would receive the energy and convert it into electrical power. These rectennas would be designed to efficiently capture the incoming energy, even from vast distances.
How Could Space-Based Solar Panels Help Solve Earth’s Power Crisis?
Unlimited, Continuous Power
SBSP offers several key advantages over terrestrial solar power, including:
- Continuous Power: Since space-based solar arrays are located above the Earth’s atmosphere, they have access to uninterrupted sunlight. Unlike traditional solar panels on Earth, which only generate power during the day and are hindered by clouds or storms, SBSP systems can function 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
- Unlimited Solar Capacity: Space-based solar arrays can gather sunlight more efficiently, as they are exposed to significantly higher levels of solar energy than solar panels on Earth. The amount of sunlight they can capture is also ten times more intense than what Earth-bound solar panels can receive, allowing for vastly greater energy production.
- No Land Use Conflicts: Unlike terrestrial solar farms that require vast amounts of land, space solar arrays would occupy no land on Earth, making them ideal for areas with limited space or high population density. This makes them especially attractive for urban areas and countries facing land scarcity for renewable energy infrastructure.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Space-based solar power could be a key component in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By providing clean energy, SBSP can lessen reliance on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to climate change.
Current Research and Development
International Efforts and Collaboration
Several nations are currently investing in SBSP research, acknowledging its long-term potential:
- NASA’s SBSP Initiative: NASA has been researching SBSP for several decades. In 2021, the space agency published a comprehensive report on SBSP’s feasibility, focusing on the key challenges and technological developments needed to make space-based solar power viable. NASA’s efforts include researching wireless power transmission and microwave beam technologies. (nasa.gov)
- ESA’s Solaris Project: The European Space Agency (ESA) launched the Solaris program in 2021 to explore space-based solar power and test its applications. The goal is to develop a demonstrator system by the mid-2030s that could pave the way for operational systems by 2040. (esa.int)
- China’s Space Solar Research: China has aggressively pursued SBSP development through the China National Space Administration (CNSA). In 2021, the country launched an experimental satellite designed to test the basic principles of SBSP. China is expected to roll out larger-scale systems as early as the next two decades.
Technological Challenges
High Costs and Engineering Barriers
Despite the promise, there are significant obstacles in the way of large-scale SBSP implementation. The most notable include:
- Launch Costs: One of the biggest barriers to SBSP is the cost of launching equipment into space. Current space missions are expensive, with launch costs running into the millions of dollars per mission. Although companies like SpaceX are driving down the cost of space access with reusable rockets, the price remains high for a large-scale SBSP system.
- Energy Conversion Efficiency: The conversion of solar energy into microwaves or laser beams is still relatively inefficient. Improving the efficiency of energy transmission in space is a key area of focus for researchers. It will be essential for these systems to convert solar energy into microwaves with minimal losses.
- Microwave Transmission and Safety: Transmitting power from space to Earth through microwaves requires precise targeting and safe energy levels. Safety protocols must be developed to prevent harm to aircraft, satellites, or even people on the ground. The transmission must be reliable and controlled, with no risk of interference to other critical communications.
- Orbital Assembly: Building large-scale solar arrays in space requires advanced space robotics and in-orbit manufacturing technologies. These capabilities are still in their infancy, requiring further development to build and maintain the necessary infrastructure in space.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Potential Environmental Impacts
While SBSP holds immense potential as a renewable energy source, it is crucial to consider its environmental impacts, especially during its early stages:
- Space Debris: Large SBSP satellites would need to be carefully managed to avoid adding to the growing problem of space debris. This could pose risks to other satellites and spacecraft.
- Energy Transmission Hazards: Beaming high-powered microwaves or lasers from space could raise safety concerns for living organisms and aircraft. Researchers are working on methods to ensure the microwave beams would be safe and directed accurately, minimizing the risk of harm.
- Lifecycle Emissions: While SBSP itself would generate clean, renewable energy, the carbon footprint of constructing and launching the required space infrastructure must be factored into overall sustainability assessments. Building and launching rockets, constructing satellites, and creating rectennas on Earth all contribute to emissions, particularly in the early stages.
The Path Forward: Is Space-Based Solar Power Feasible?
Long-Term Prospects
While SBSP is not ready for commercial deployment, the continued research and development efforts suggest it could become a mainstream solution by the mid-21st century. The gradual reduction of launch costs, improvements in wireless power transmission, and the development of advanced space manufacturing systems are key to its eventual success.
Experts believe that SBSP should be viewed as complementary to terrestrial energy solutions, such as solar and wind power. Instead of replacing ground-based solar farms or wind turbines, SBSP could provide continuous baseload power to supplement intermittent renewable sources.
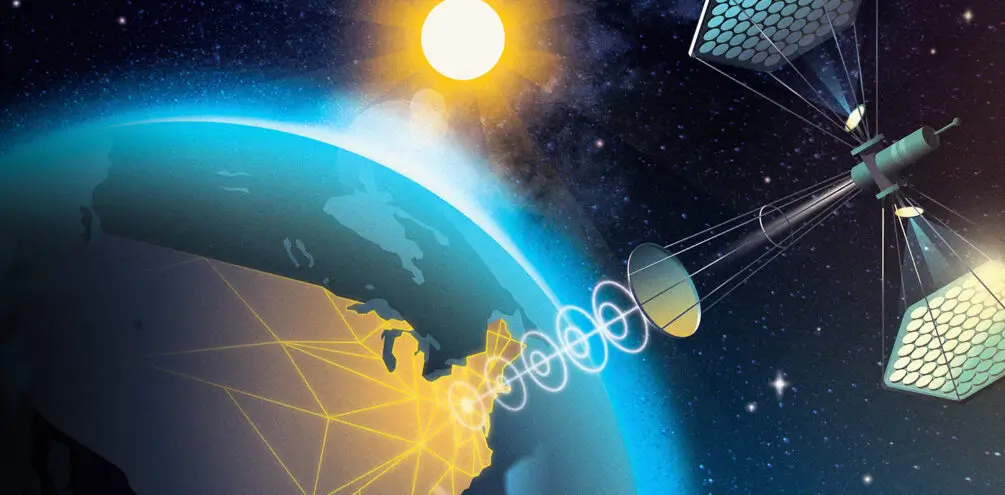

Space-based solar power represents an exciting, long-term solution to Earth’s energy needs. Although there are significant engineering, economic, and safety hurdles to overcome, SBSP has the potential to provide continuous, clean energy for a rapidly growing global population.
If successful, space solar power could help solve the energy crisis while reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, making a meaningful contribution to global climate goals.
FAQs
What is space-based solar power?
Space-based solar power is the concept of collecting solar energy from satellites in space and transmitting it to Earth using microwave beams, providing a continuous energy source.
How is SBSP different from traditional solar power?
Unlike Earth-based solar, which is affected by the time of day and weather conditions, SBSP operates 24/7, collecting energy from space and transmitting it without any interruptions.
What are the challenges of implementing SBSP?
Key challenges include high launch costs, inefficiencies in energy conversion and transmission, the need for advanced space robotics, and ensuring safety during the energy transmission process.








